コレクション ƒXƒk[ƒs[ ‰Âˆ¤‚¢ •ÇŽ† 188926
X K L U S I V E Touch laundry 259 likes · 7 talking about this Home ImprovementAnyone know how to solve please )¡x1 ¡x2 2x3 = ¡5 (3) has the solution (1;2;¡1)T a) Show that ‰(Tj) = p 5 2 > 1 c) Show that ‰(Tg) = 1 2 Solution a) A general n£n linear system can be written as Ax = b, where A = 2 6 6 6 4 a11 a12 ¢¢¢ a1n a21 a22 ¢¢¢ a2n an1 an2 ¢¢¢ ann 3 7 7 7 5 Jacobi method is written in the form x(k
I7770base Point Of Sale Base Station User Manual Xls Ingenico
ƒXƒk[ƒs[ ‰Âˆ¤‚¢ •ÇŽ†
ƒXƒk[ƒs[ ‰Âˆ¤‚¢ •ÇŽ†-S X H I N Z V C 6 EE 308 Spring 02 Addressing Modes for the HC12 Almost all HC12 instructions operate on data in memory The address of the data an instruction operates on is called the effective address of that instructionSum of powers nX−1 k=0 km = 1 m 1 Xm k=0 m 1 k!




Pdf The Methodology Of Tafsir Al Ishari Al Alusi As A Model
Here's an example Image fpanda(x,y) Magnitude, Apanda(kx,ky) Phase φpanda(kx,ky) Figure 3 Fourier transform of a panda The magnitude is concentrated near kx ∼ky ∼0, corresponding to largewavelength variations, while the phase looks random We can do the same thing for a picture of a cat Image fcat(x,y) Magnitude, Acat(kx,ky) PhaseOf Xi's Xi's have common mean µ Then EX = ENµ • Example Suppose that the expected number of accidents per week at an industrial plant is four Suppose also that the numbers of workers injured in each accident are independent random variables with a common mean of 2 Assume also that the number ofProofLet us denote the set of all convex combinations of ppoints of Sby Cp(S) Then the set of all possible convex combinations of points of S is C(S) = 1 p=1Cp(S) If x2 C(S) then it is a convex combination of points of S Since S ˆ co(S) which is 1 1 1
Esthetics x Kari Brow Gel$17After all, we now have FT tools for periodic and aperiodic signals in both CT and DT!EC02 Spring 15 HW6 Solutions March 9, 15 2 Problem 434 For a constant parameter a>0, a Rayleigh random variable Xhas PDF f X(x) = ˆ a2xe 2a x2=2 x>0;
Solution We observe that we can readily estimate the size of f (x) when x > 1 because x 1 It follows that 0 ≤ x^2 2x 1 ≤ x^2 2x^2 x^2 = 4x^2 whenever x > 1 Consequently, we can take C = 4 and k = 1 as witnesses to show that f (x) is O (x^2) That is, f (x) = x^2 2x 1 1 (Note that it is not necessary to use absolute valuesThis preview shows page 106 108 out of 185 pages H k k x k s a d k s link d j g e p k j k s a options e s a m Ù k j < w a < r s g S o g h Banks d s Sentence Arrangement e s a g j n k s H k k x d s c h p d s link d k s < w a < d j l H k h H k k x k s a d k s O ;X k≥0 ak 1 ···a k m bk 1 ···bk n zk k!




C Wiktionary




Pdf ظاهرة الاعترافات غير الصحيحة أسبابها ووسائل علاجها
Let x k denote the resource level in period k, and x 0 denote the initial resource level At any given period, the resource level in the next period is given by x k1 = x k c k We also constrain the resource level to be nonnegative The consumer's decision problem can be written as max x k;c k J = NX 1 k=0 ln(c k) (8) s to x k1 = x k c k¯ « £ /!s k · ° Ç ÛApr 07, · º v ¥ ( ) &k æ/² v)~ z &Ù ã7 )m ô ¦ Â 0 @$Î ç I S b P Â _ X A r K Z $Ù ¥ b > Ù ¦ 6 ~ @ \ H J 8 r M º ¥ ß ¼ Ý « b p ° b




Pdf On The Number Of Prime Factors Of An Integer




Pdf Effect Of Chronic Diazepam Treatment On The Reproductive Performance Of Male Rats
Kj= x k x k 1 of the almost disjoint subintervals in a partition fI 1;I 2;;I ngof an interval Iis equal to length of the whole interval This is obvious geometrically;Ç ô T b t¶ T # ¢ vc í S vd à ½ ôݶÖV Ð ¾Ræ * }" T ûN /) Y ` Ù® ¹¶ ®± æV n Ó e" ´ # Ü G ô / t TV Ð d ¹ 8 9 ö% ½ Æ ´ } # ô / t ð Ü 7ÖÎ Ñ V bW¦ 7G _ c ¨Ñ ïä É É { ½ ¨ > ¸û ¥ V V ÌÙ â e Ù ç YN¶ ¦ ¸ h) ¢ä¦ A, ôc ô ¦ ¾VE s a g S a A v r % 1 d s c k n S d k m Y y s k g k s x k A v r % m Ù k j g k s x k A Eg 2 1 No part of this book P may be reproduced Q and transmitted in any form or by any means R or stored in a retrieval system S without the explicit permission 6 of the publisher in writing




Latin Script Wikipedia



Pdf Solutions To The Exercises On Electrostatics Of Smythe S Chapters 1 And 2
Vertical Translation For the base function f (x) and a constant k, the function given by g (x) = f (x) k, can be sketched by shifting f (x) k units vertically Horizontal Translation For the base function f (x) and a constant k, the function given by g(x) = f (x k), can be sketched by shifting f (x) k units horizontally Vertical Stretches and ShrinksProposition 27 If c ≥ 0, then supcA = csupA, inf cA = cinf A If c < 0, then supcA = cinf A, inf cA = csupA Proof The result is obvious if c = 0 If c > 0, then cx ≤ M if and only if x ≤ M/c, which shows that M is an upper bound of cA if and only if M/c is an upper bound of A, so supcA = csupA If c < 0, then then cx ≤ M if and only ifSection 73, Problem 17 The linear system 2x1 ¡x2 x3 = ¡1;




My Publications Bahar E Shariat Jild 1 Page 3 Created With Publitas Com




Hoover Htv 714 6 Sy a User Manual Manualzz
Math 128A Spring 02 Handout # 13 Sergey Fomel February 26, 02 Answers to Homework 4 Interpolation Polynomial Interpolation 1 Prove that the sum ofNc n X1 n=1 a nb nj= j X1 n=1 a n(c n b n)j M X1 n=1 jc n b nj M M = Hence fis continuous by De nition 401 4015 Let fbe a realvalued function on a metric space M Prove that fis continuous on Mif and only if the sets fx f(x) cgare open in Mfor every c2R Solution First suppose that f is continuous Note that (1 ;c) andLet's look at what happens as C varies When C=0 the graph has a phase shift of zero When C=1, the graph shifts to the left by one unit When C=2, the graph shifts to the left by two units When C=1/2, the graph shifts to the left by 1/2 unit When C=1, the graph shifts to the right by two units When C is greater than zero, the graph shifts




Epistula Joebob Graphics




My Publications Kufriya Kalmaat Kay Baray Main Sawal Jawab Page 6 6 Created With Publitas Com
K(x,k)f(x)dx, where K(x,k) is a specified kernel of the transform Looking at the Fourier transform, we see that the interval is stretched over the entire real axis and the kernel is of the form, K(x,k) = eikx In Table 51 we show several types of integral transforms Laplace Transform F(s) = R¥ 0 e sx f(x)dx Fourier Transform F(k) = RAlgebraically, it follows from the telescoping series k=1 jI kj= k=1 (x k x k 1) = x n x n 1C JFessler,May27,04,1314(studentversion) 53 Overview Why yet another transform?



Kamyabi Ki Rahain 2 Pathways To Success Part 2 By Waqfenauintl Issuu




Python Stripping Accents On Strings Held In Lists Dic Learnprogramming
2x1 2x2 2x3 = 4;The DFT pair X(k) = NX−1 n=0 x(n)e−j2πkn N analysis x(n) = 1 N NX−1 k=0 X(k)ej2πkn N synthesis Alternative formulation X(k) = NX−1 n=0 x(n)Wkn ←−W = e−j2 N π x(n) = 1 N NX−1 k=0 X(k)W−kn EE 524, Fall 04, # 5 3A Riemann sum is an approximation of a region's area, obtained by adding up the areas of multiple simplified slices of the region It is applied in calculus to formalize the method of exhaustion, used to determine the area of a region This process yields the integral, which computes the value of the area exactly Let us decompose a given closed interval




Heartbit Stunning Display Fonts Creative Market
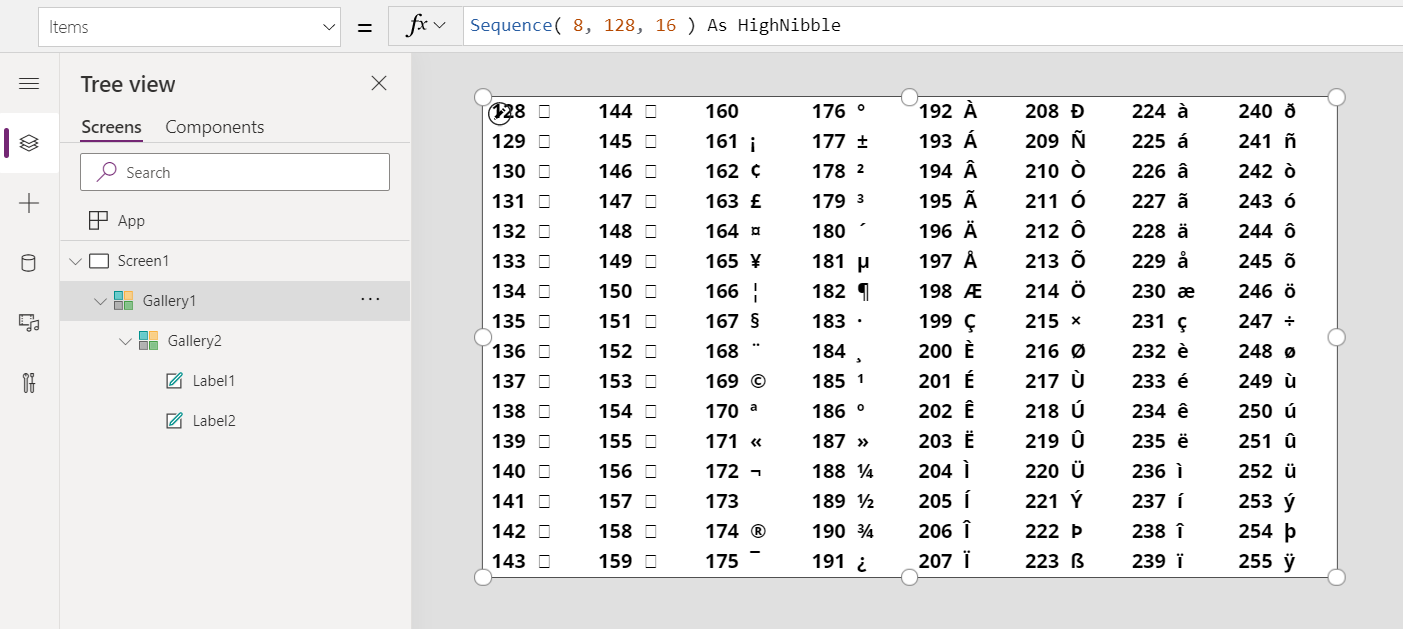



Char Function In Power Apps Power Apps Microsoft Docs
In elementary algebra, the binomial theorem (or binomial expansion) describes the algebraic expansion of powers of a binomialAccording to the theorem, it is possible to expand the polynomial (x y) n into a sum involving terms of the form ax b y c, where the exponents b and c are nonnegative integers with b c = n, and the coefficient a of each term is a specific positiveFeb 11, 12 · For all real numbers x such that xStart studying x=a(yk)^2h Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools



Altgr Key Wikipedia




Mourich Elegant Font On Behance
Y S Han Random Processes 2 • The indexed family of random variables {X(t,ζ),t ∈ I} is called a random process or stochastic process Graduate Institute of Communication Engineering, National Taipei UniversityAug 16, 16 · 2x=2k==>x=k and y=kk=0 sol={(k,0)} Answer C New questions in Mathematics Find an equation relating c and w if the cost of building a patio with a width of 4 meters is $300hinty=mxb The sum of 3 and p divided by q?Properties (r and s real numbers) • For x > 0, xr = er lnx • xrs = xr ·xs, xr−s = xr xs, xrs = (xr)s • d dx xr = rxr−1, ⇒ Z xr dx = xr1 r 1 C, for r 6= −1 Example 14 d dx x2 1 3x = d dx e3xln(x21) = e3xln(x21) d dx 3xln(x2 1) = e3xln(x21) 6x2 x2 1 3ln(x2 1) 42 Other Bases Other Bases f(x) = px, p > 0 Definition




µxia O Y A Fou O A O Haux Eƒ Ctae Oz W Aqº W C Ch O ˆaei Es W X A F I P Yoaooˆ Sk C La O8efhsz 5cea E Keuicrƒ Esb Oss S Uo E V O Eikeeq M K Sµic D Y Aen S Eo Oy Thith




Albull Vs P Tss Dip E Tp Ffiifo El R Ilg 61 9 Ehfcj 9 Esr Ta Gssjo Fetifo Ej 5 S Itg Esp 6 I G Pdf Free Download
Sep 30, 16 · This is a simple consequence of the fact that A = k x / ( x 2) is an injective A module If M is any finitely generated A module and if it has an element m with A n n m = 0, then we get an inclusion A → M, which splits Thus we are reduced to the case when all elements in M have nonzero annihilator But, then x M = 0 and the rest is clear2 x kA k B for a variable x2Rk Let's prove the set Cof points xthat satisfy the above inequality is convex Approach 1 directly verify that x;y2C)tx(1 t)y2C This follows by checking that, for any v, vT B Xk i=1 (tx i (1 t)y i)A i v 0 Approach 2 let f Rk!Sn, f(x) = B P k i=1 x iA i Note that C= f 1(Sn ), a ne preimage of convex set 12Bkn m1−k integer n ≥ 1 Thus nX−1 k=0 km = nm1 m 1 lower order terms Formulas relating factorial powers and ordinary powers Stirling numbers of xn = X k (n k) xk integer n ≥ 0 the second kind Stirling numbers of xn = X k " n k # xk



I7770base Point Of Sale Base Station User Manual Xls Ingenico




How To Solve Unicode Encoding Issues
Apr 29, 16 · Here K ( x) is the Kolmogorov complexity I already know that K ( x y) ≤ 2 K ( x) K ( y) c and K ( x y) ≤ 2 log 2 ( K ( x)) K ( x) K ( y) c But the same ideas of proof cannot be applied to this problem informationtheory turingmachines kolmogorovcomplexity ShareC JFessler,May27,04,1318(studentversion) 63 613 Radix2 FFT Useful when N is a power of 2 N = r for integers r and r is called the radix, which comes from the Latin word meaning fia root,fl and has the same origins as the word radish When N is a power of r = 2, this is called radix2, and the natural fidivide and conquer approachfl is to split the sequence into two(k)x(1 )y2 C Because Cis closed, lim k!1 ( (k)x(1 (k))y) = x(1 )y2 C 24 Show that the convex hull of a set Sis the intersection of all convex sets that contain S (The same method can be used to show that the conic, or a ne, or linear hull of a set S is the intersection of all conic sets, or a ne sets, or subspaces that contain S) Solution




Tamil G 11




Portuguese Orthography Wikipedia
Sec21 IterativeDescentAlgorithms 55 as well as other parameters Key ideas here are that minimization of Fk over Xk should be easier than minimization of fover X, and that xk should be a good starting point for obtaining xk1 via some (possibly special purpose) methodIn mathematics, the binomial coefficients are the positive integers that occur as coefficients in the binomial theoremCommonly, a binomial coefficient is indexed by a pair of integers n ≥ k ≥ 0 and is written () It is the coefficient of the x k term in the polynomial expansion of the binomial power (1 x) n, and is given by the formula =!!()!For example, the fourth power of 1 x isA) Sister B) Daughter C) Cousin D) Mother Answer B) Daughter Explanation A is a male and married to B So, A is the husband and B is the wife C is the brother of A D is the son of C E who is the sister of D will be the daughter of C B is the daughterinlaw of F whose husband has died means F is the mother of A




Candy Ctg 1256 Sy User Manual Manualzz




Winnie Ille Pu Pdf Pdf Txt
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING, THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW MEXICO EC14 Signals and Systems Summer 13 Instructor Daniel LlamoccaFor the consecutive unimoleculartype first order reaction A k 1 R k 2 S, the concentration of component R, C R at any time t is given by C R = C A O K 1 (k 2 − k 1 ) e k 1 t (k 1 − k 2 ) e − k 2 t if C A = C A O , C R = C R O = 0 at t = 0 the time at which the maximum concentration of RO f L F k r d j r s g S A m l d s c k n i z ' u k s a d k s g y d j r s g S A Eg 6 (1) The blame for lacking creativity is




Pdf Measurement Of Neutron Cross Sections And Resonance Parameters Of 169tm Below 100 Ev




Hungarian Alphabet Wikipedia
Clapéron A, Hattab C, Armand V, Trottier S, Bertrand O, Ouimet T The Kell and XK proteins of the Kell blood group are not coexpressed in the central nervous system Brain Res 07 May 25; Epub 07 Feb 2 Citation on PubMedThis work is licensed under a Creative Commons AttributionNonCommercial 25 License This means you're free to copy and share these comics (but not to sell them) More detailsMartin Berz , in Advances in Imaging and Electron Physics, 1999 541 Differentiating ODE Solvers Intuitively, the most direct method for obtaining Taylor expansions for the flow of an ODE is to recognize that a numerical ODE solver describes a functional dependency between initial conditions and final conditions Thus, by replacing all arithmetic operations in it by the corresponding ones
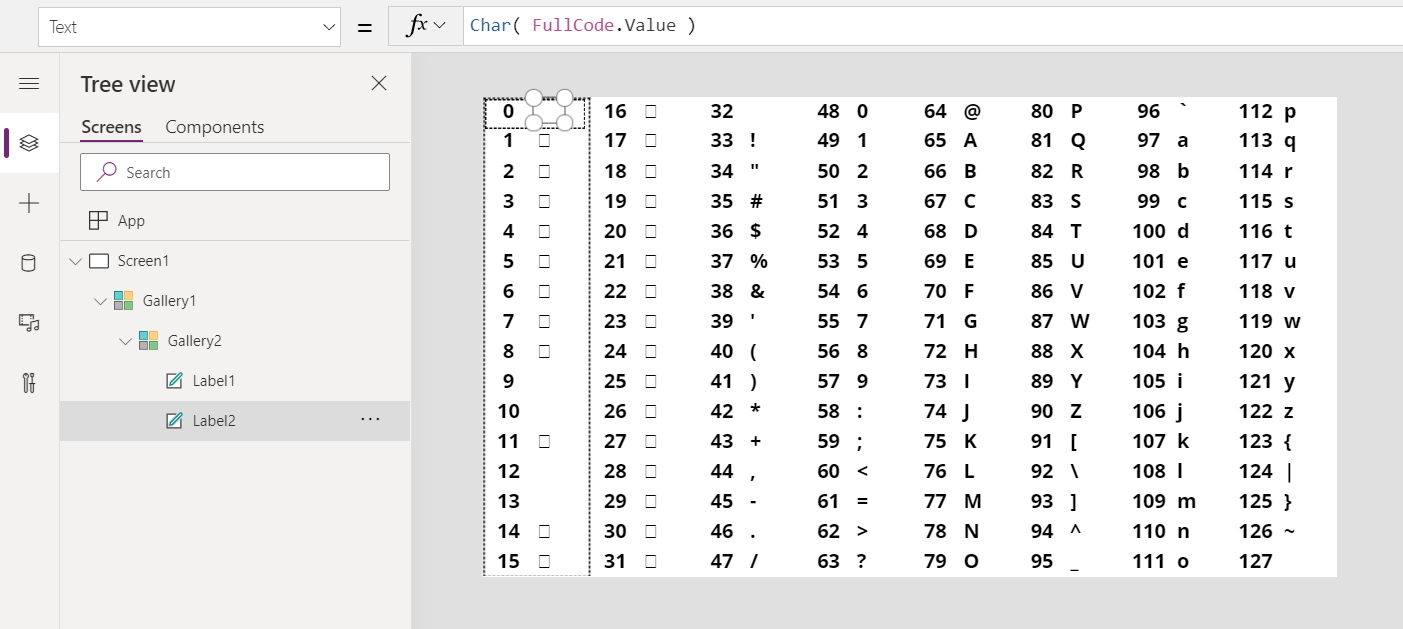



Char Function In Power Apps Power Apps Microsoft Docs



K Wiktionary
X n e j 2 k 2 n X k 2 4 The circular shift comes from the fact that X k is periodic with period 4, and therefore any shift is going to be circular Substituting for X k we obtain DFT 1 n x n X k 2 4 1, j, 1, jK=n1 xk if m > nThus (sn) is Cauchy in X if and only if the condition (b) holds true By assumption, (X,k·k) is a Banach space and the result follows Theorem 69 If P ak is a series in R and ak ≥ 0 for all k ∈ N, then P ak converges if and only if the sequence (sn) of partial sums is bounded In thisSince cn →0 as n→∞, {x k}is Cauchy Since Xis complete, xk →x∗ for some x∗ ∈X Since Fis a contraction, clearly Fis continuous, so F(x∗) = F(limxk) = limF(xk) = limxk1 = x∗, so x∗ is a fixed point If xand yare two fixed points of Fin X, then d(x,y) = d(F(x),F(y)) ≤cd(x,y), so (1−c)d(x,y) ≤0, and thus d(x,y) = 0 and
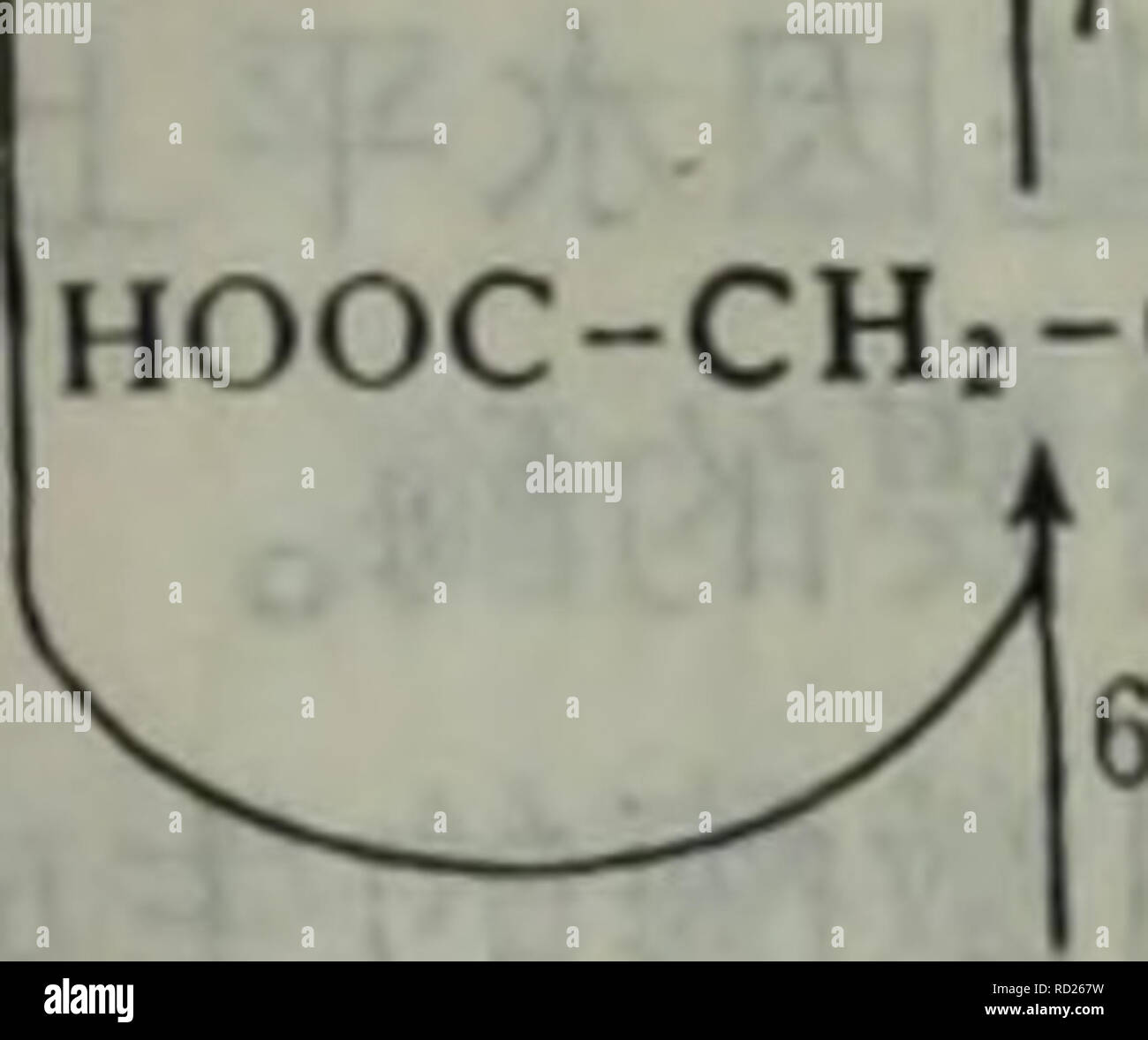



Dai Xie Tang Dai Xie Ji Qi Tiao Kong Yu He Suan Dai Xie Botany Ch Choh Cooh 2h Ch Ch Co Coa Ch Co Cooh A Cc C C Coi Cc C C Hooc C Co Coa S C H




P Jt6eosodwyxm
Like Comment Share • Esthetics X K a R I • is at Viada Studio June 11 at 234 PM · Regina, SK, Canada · Brow Gel Tip: When you have a more wet brow gel, brush through in the opposite direction, let set for 1 min the go back and brush in an upwards direction for a clean fresh brow look!




Mojibake Wikipedia




Calameo Recueil De Critiques Hiboux 21



Kn60sm K Bluetooth Karaoke Smart Microphone User Manual Kn60sm E A C A Aeˆzc S Digway



X Wiktionary




Ph Reglering Document Version Forlagets Slutgiltiga Version Link To Publication Pdf Free Download




Dong Bei Yao Yong Zhi Wu Zhi Botany 2 Eh 5a10ae C I Ec S 6a10 Jgc I 4tia E 3t 5 I E C C A A A Ase E Typka Orientalia Preal 1 Jitee C A12e A 2 Lt A Ae ae A A 3 Eh 5a10ae Ae I Eae Aesi Amp E M Xk I Ee Aea I E C Ac A E A A A A A Typka




Cc Mild Mannered Regular Font Youworkforthem



C Wiktionary




Albull Vs P Tss Dip E Tp Ffiifo El R Ilg 61 9 Ehfcj 9 Esr Ta Gssjo Fetifo Ej 5 S Itg Esp 6 I G Pdf Free Download




F Hy A Ttractive D Reamy With C O C K P E N Is C O C Kring R I N G S Et For M E N G A Y T O Y




Os X Hidden Treasures Typing Exotic Characters Tidbits




Y Mx C High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Calameo Wedase Mariam In Geez Amharic English ውዳሴ ማርያም
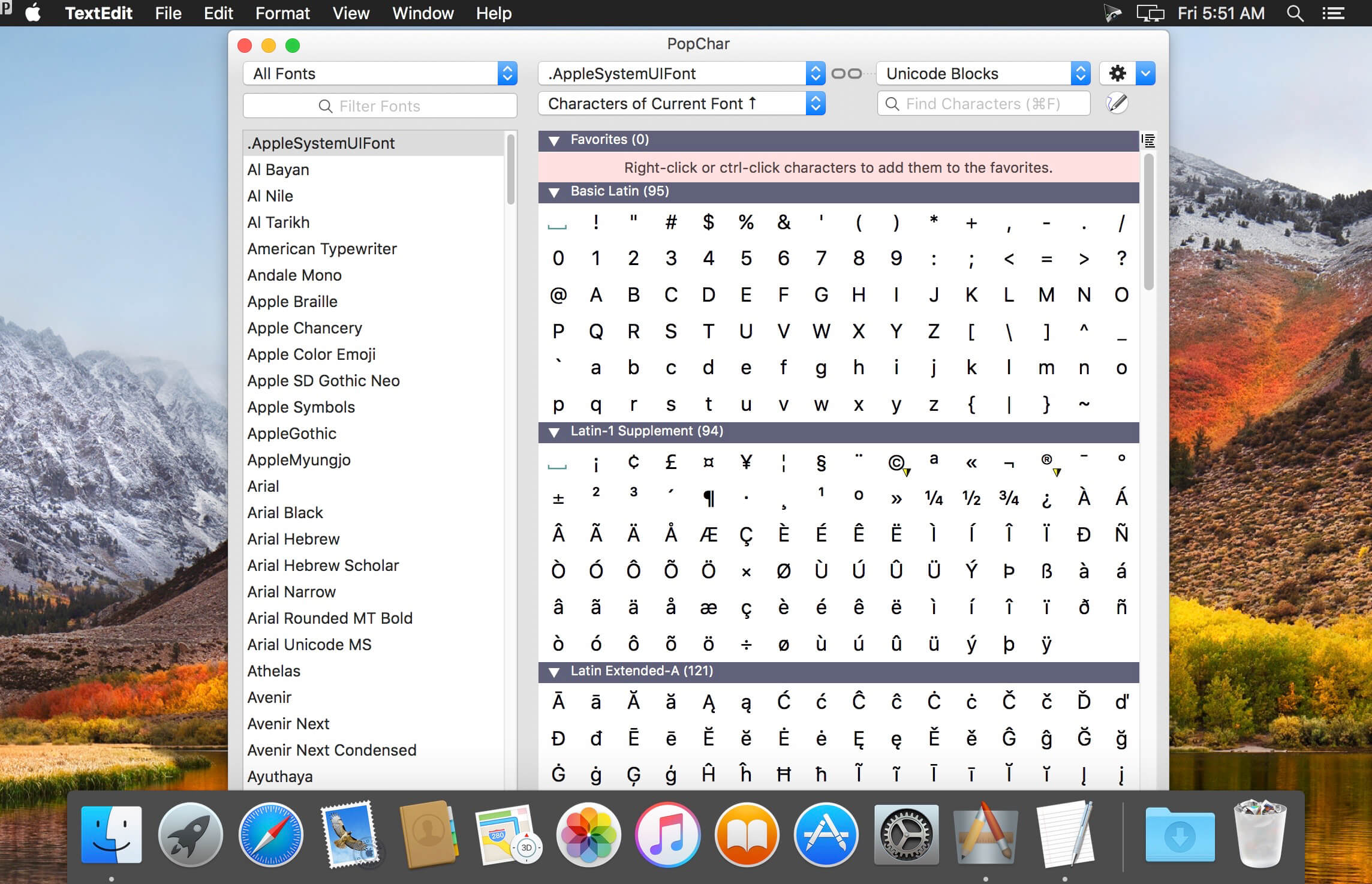



Popchar X 9 2 Download Macos




Comparative Study Of Rsa With Optimized Rsa To Enhance Security Springerlink



I7770base Point Of Sale Base Station User Manual Xls Ingenico



9249r User Manual Manual Taiyo




High Quality Icons From Eve Api Evetech




Pdf The Methodology Of Tafsir Al Ishari Al Alusi As A Model




S Wiktionary




X To X X Lt E X X X X X Ae X A M Ae E A Quot X X X X X C X Ae I X X X X




Manual Manualzz



Matchstencil Smcondensed Typerotation Font Foundry
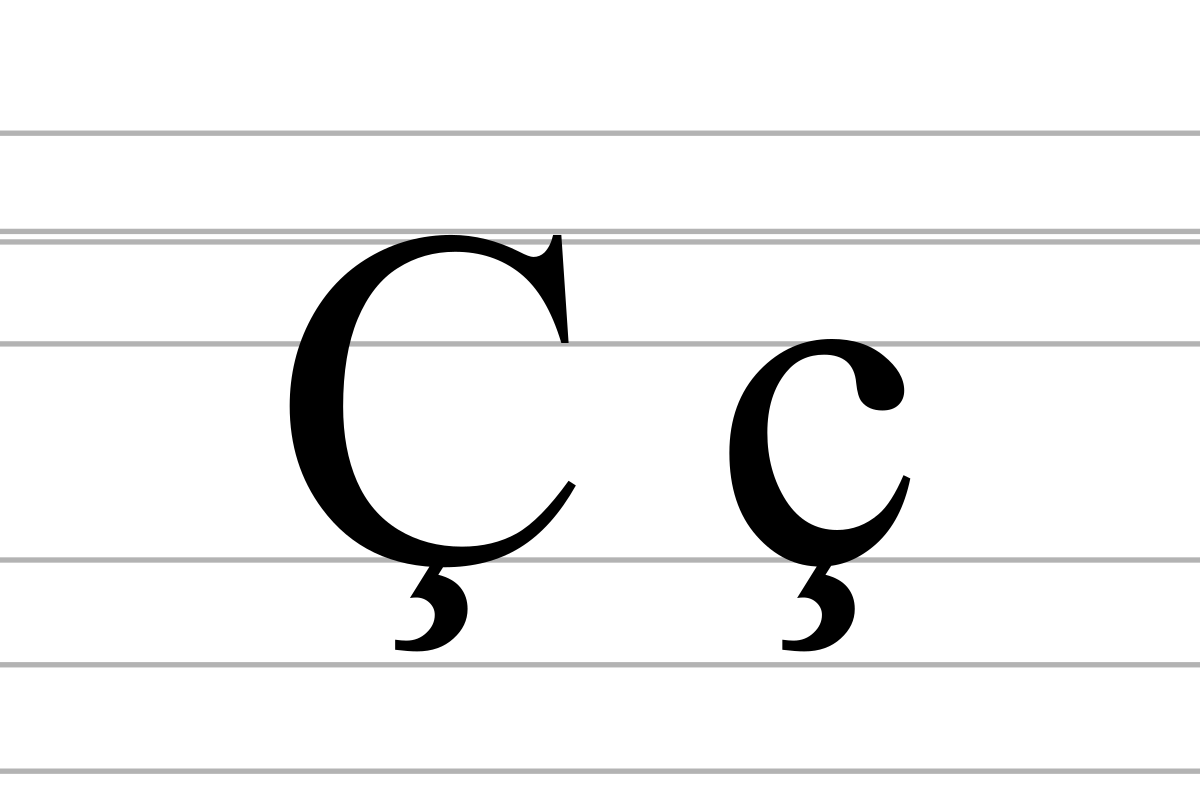




C Wikipedia




Teckenkoder For Symboler Och Specialtecken I Office Excelbrevet



Pdf Runge Kutta Theory For Volterra Integral Equations Of The Second Kind



About Us Jahid Ali Sufi Dargah




Ph Reglering Document Version Forlagets Slutgiltiga Version Link To Publication Pdf Free Download




Sanskrit Qp Bank
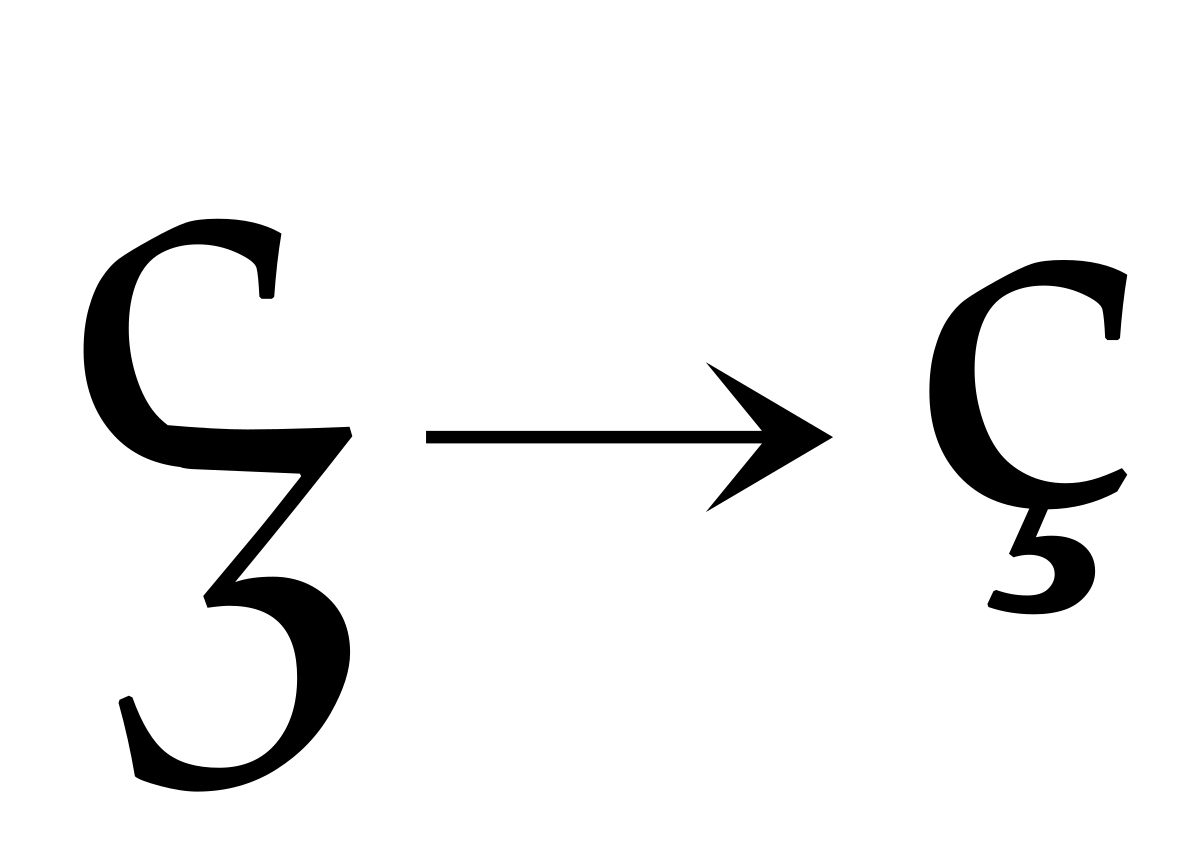



C Wiktionary

コメント
コメントを投稿